



Next: The .mtz wrapper
Up: Using the program
Previous: Testing the executable
Contents
Supported crystallographic calculations
GraphEnt automatically recognises the following types of syntheses :
- F2 Patterson synthesis, defined by
h, k, l, F,
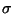 (F)
(F)
-
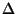 F2 difference Patterson synthesis, defined by
h, k, l, F1,
F2 difference Patterson synthesis, defined by
h, k, l, F1,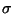 (F1), F2,
(F1), F2,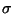 (F2). The function calculated
is the one commonly used for isomorphous difference Patterson maps
with an amplitude of
F = (F1 - F2)2 and a standard deviation
(F2). The function calculated
is the one commonly used for isomorphous difference Patterson maps
with an amplitude of
F = (F1 - F2)2 and a standard deviation
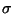 (F) = 2
(F) = 2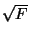
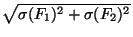 +
+ 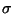 (F1)2 +
(F1)2 + 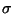 (F2)2.
(F2)2.
- Phased Fourier synthesis without FOM, defined by
h, k, l, F,
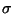 (F),
(F),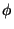
- Phased Fourier synthesis with FOM, defined by
h, k, l, F,
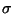 (F),
(F),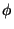 , FOM
, FOM
All other types of syntheses that can be reduced to any of the above are also supported but
the reduction step is a user's responsibility.
For example, to calculate a
(2Fo - Fc)exp(i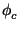 )
map you would have to prepare a column containing the
(2Fo - Fc) term by yourself, and
give the program six columns of the type
h, k, l,(2Fo - Fc),
)
map you would have to prepare a column containing the
(2Fo - Fc) term by yourself, and
give the program six columns of the type
h, k, l,(2Fo - Fc),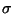 (2Fo - Fc),
(2Fo - Fc),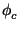 . For CCP4
users this is easily (and interactively) achieved with the program sftools9.
. For CCP4
users this is easily (and interactively) achieved with the program sftools9.
Footnotes
- ... sftools9
-
I should add here that for some of the more complex syntheses, the most difficult part
of setting-up the calculation
appears to be the propagation of errors, ie calculating correctly the
standard deviation of the amplitude terms.




Next: The .mtz wrapper
Up: Using the program
Previous: Testing the executable
Contents
NMG, Nov 2002